test lcl tear|lcl tear symptoms in knee : commercial Varus Stress Test- The most useful special test when assessing a LCL injury. With the femur stabilized, a varus force is applied with special attention to the lateral joint line. The test is first performed in 30 degrees flexion. Increased . Step inside to meet our professional Live Dealers, show them what heroes are made of .
{plog:ftitle_list}
10 de ago. de 2022 · Though not as efficient or effective as live chat, email is one of the best methods for contacting Bet365 customer service. There’s a main Bet365 email address .
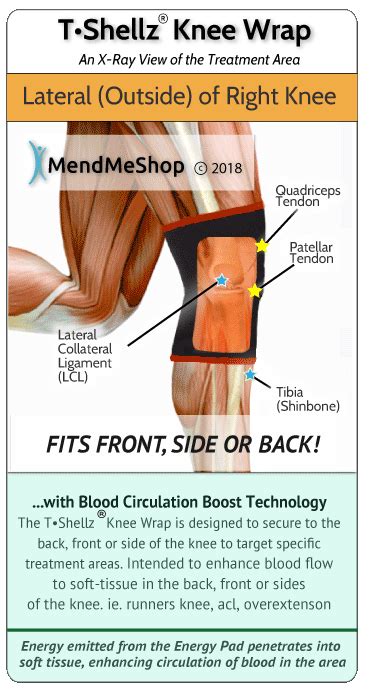
While most LCL tears can be diagnosed without medical imaging, a doctor may order an x-ray or MRI to rule out other possible injuries and to determine the severity of an LCL tear. X-ray. An x-ray shows bones and can help determine . Lateral Collateral Ligament (LCL) injuries of the knee typically occur due to a sudden varus force to the knee and often present in combination with other ipsilateral ligamentous knee injuries (ie. PLC, ACL). Diagnosis can . The lateral collateral ligament (LCL), also known as the fibular ligament, is one of the knee joint's key stabilizers (see Image. Left Knee Ligaments). This fibrous structure .
bond line thickness measurement
Varus Stress Test- The most useful special test when assessing a LCL injury. With the femur stabilized, a varus force is applied with special attention to the lateral joint line. The test is first performed in 30 degrees flexion. Increased .If the varus stress test is positive at 20°, but negative at 0°, only the LCL is torn. A positive result at both 0° and 20° indicate cruciate ligament involvement. [13]Diagnosis of an LCL Injury. Your health care provider will first conduct a lateral collateral ligament test to reveal any looseness in the ligament. This test involves bending the knee to 25 degrees and placing pressure on the inside surface of .This test assesses the severity of LCL injuries with more than 90 percent accuracy. It's often used to confirm the ligament injury diagnosis and to check for injuries to cartilage or other knee .
In this video, we are demonstrating a Lateral Collateral Ligament (LCL) Injury Assessment, which looks for pain and injury to the outside knee. This test sho.
The lateral collateral ligament, or LCL, is one of the four major knee ligaments.The LCL connects the end of the thigh bone (the femur) to the top of the smaller shin bone (fibula), on the outside of the knee. The LCL helps to . An LCL injury (a torn LCL or a LCL tear) is a strain or tear to the lateral collateral ligament (LCL). The LCL is a band of tissue that runs along the outer side of your knee . Isolated injuries of the lateral collateral ligament (LCL) are among the least common knee injuries but can occur when the joint is struck from the inside (varus stress). More commonly, and typically as the result of more significant trauma, the LCL is injured along with other structures, often including those of the posterolateral corner of .
Lateral Ulnar Collateral Ligament Injury is a ligamentous elbow injury usually associated with a traumatic elbow dislocation, and characterized by posterolateral subluxation or dislocation of the radiocapitellar and ulnohumeral joints. . forearm supination, axial loading, valgus (posterolateral) stress, and elbow extension causes progressive . Lateral ligament sprains are categorized into grades 1, 2, or 3 depending on the extent of your injury. Grade 1 LCL sprain. . However, you will feel pain with the varus stress test (see below), but no joint laxity. Grade 2 LCL sprain. With a grade 2 LCL sprain, you will have significant tenderness on the outside of your knee. You will likely .These are often contact injuries, but not always. Medial collateral ligament tears often occur as a result of a direct blow to the outside of the knee. This pushes the knee inward (toward the other knee). Blows to the inside of the knee that push the knee outward may . A lateral collateral ligament (LCL) tear is a knee injury that seldon happens in isolation. The force that causes it is usually so big that often something else also gets injured. This article explains how the LCL typically gets injured, what the symptoms are, how the injury is diagnosed and graded, what the treatment options are, and what the recovery times might be .
Medial collateral ligament (MCL) and lateral collateral ligament (LCL) sprains are knee injuries. The MCL is the ligament located on the inside of your knee joint . It links your thighbone (femur) and shinbone (tibia).
Diagnosis can be suspected clinically with presence of a traumatic knee effusion with increased laxity on Lachman's test but requires MRI studies to confirm diagnosis. . PCL, LCL/PLC injuries. chronic ACL deficient knees associated with. chondral injuries . complex, unrepairable meniscal tears and bucket handle medial meniscus tears . Anatomy. Your doctor will diagnose your injury by examining the area for swelling and by performing an LCL tear test. The test will consist of gently moving the knee in different directions to find the source of the symptoms. LCL Tear Treatment Options. Even for severe LCL tears, the treatment process begins with immediate attention and continued at . On physical exam, anterior and posterior drawer test are negative. He has increased laxity with valgus stress and no laxity with varus stress to the knee. Introduction. Collateral ligaments of the knee include the. lateral collateral ligament (LCL) medial collateral ligament (MCL) . increased laxity with varus stress suggests an LCL injury .
A second test may be performed to examine the medial collateral ligament namely the Swain test. This test examines the chronic injury and rotatory instability of the knee. The test is performed by flexing the knee into 90 degrees and externally rotating the tibia. . (ACL) injuries, bone bruises, lateral collateral ligament injuries (LCL .
positive test is a subjective apprehension, instability, or pain at the MCL origin between 70 and 120 degrees . LCL injuries. lateral pivot-shift test . patient lies supine with affected arm overhead; with shoulder fully externally rotated, forearm is supinated and valgus stress is applied while bringing the elbow from full extension to flexion. Mid-substance tears can cause tenderness at the medial joint line, which can be confused with a medial meniscus injury. Distal MCL tears can cause tenderness at its attachment to the medial tibial condyle, which can be confused with pes anserine bursitis. Valgus stress testing is the best way to test the integrity of the MCL directly.
Positive Finding: A positive test occurs when gapping or pain is noted with this test in full knee extension; this may suggest both an LCL and cruciate injury. With the knee at 20 to 30 degrees of flexion, a positive test occurs when pain is noted along the lateral knee or gapping is present.Grade 1 Tears. A partial-thickness LCL tear is where only a portion of the ligament is torn. On ultrasound or MRI, a portion of the LCL would be torn but the remaining fibers would be normal. Grade 2 Tears. A grade 2 LCL tear . A lateral collateral ligament (LCL) sprain occurs when there is a tear in the ligaments on the outside of the knee. . This test does not show ligament injuries, but it may help determine whether . Lateral collateral ligament assessment (varus stress test) The lateral collateral ligament (LCL) assessment involves the application of a varus force to assess the integrity of the LCL of the knee joint. . McMurray’s test is used to assess the menisci for evidence of a meniscal tear. This test is not usually expected in an OSCE scenario as .
Check out this great test for analysing the integrity of the LCL or Lateral Collateral Ligament of the Knee Joint! The video teaches you the methodology, and.An LCL tear occurs when the knee bends inwards excessively or quickly and strenuously. This results in the LCL stretching too far which can lead to the LCL tearing or rupturing. LCL tears are graded on a scale of one to three in their severity, as are other ligament tears. Grade 1 LCL Tear. A grade one tear is an incomplete tear of the LCL. The test helps clinicians diagnose LCL injuries and choose the right management approach. Treatment options range from physical therapy to surgery, depending on the injury’s severity and symptoms. The varus stress test, along with other tests and MRI scans, guides clinicians in planning treatment and rehabilitation for knee injuries .Purpose [edit | edit source]. The valgus stress test, also known as the medial stress test, is used to assess the integrity of the medial collateral ligament (MCL) of the knee. MCL injuries are common in the athletic population and can occur as either isolated injuries, or combined with other structural injuries .. Technique [edit | edit source] Patient Position [edit | edit source]
bottle thickness measuring equipment
The lateral collateral ligament (LCL) is the ligament located in the knee joint.Ligaments are thick, strong bands of tissue that connect bone to bone. The LCL runs along the outside of the knee . Th LCL plays an important role in stabilizing the knee. Activities that put stress on this ligament, such as bending, twisting, or quickly changing direction, may lead to injuries of varying . LCL Injury of the Knee . Meniscal tears are common sports-related injuries in young athletes and can also present as a degenerative condition in older patients. Diagnosis can be suspected clinically with joint line tenderness and a positive McMurray's test, and can be confirmed with MRI studies.
why does my lcl hurt
brake disc thickness measuring tool
lcl tear test at home
lcl tear symptoms in knee
WEBApostar com 6 dezenas = R$12,00. Apostar com 7 dezenas = R$42,00. Apostar com 8 dezenas = R$112,00. Apostar com 9 dezenas = R$252,00. Apostar com 10 dezenas = R$504,00. Apostar com 11 dezenas = .
test lcl tear|lcl tear symptoms in knee